Thin film resistors, made of deposited (such as sputtered) homogeneous metal thin film, have smooth electron flow, small temperature coefficient of resistance, and long term stability and fit for high precision application.
Monolithic structure with smooth electron flow
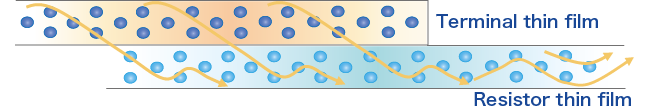
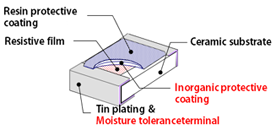
In order to further improve moisture tolerance, our terminals also have innovative thin film structure. Therefore, Susumu’s RG series are extremely robust, reliable and stable and widely used for automotive electronics.
Double layered protective coating・
Inorganic film
Innovative moisture tolerant terminal
Thin film resistors, due to their continuous even metal structure, compared to thick film resistors, have smaller resistance tolerance and temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR)
| Performance | Typical thick film resistors | Susumu thin film resistors |
|---|---|---|
| Resistive tolerance | ±0.5%,1% (precision) |
±0.01%,0.05%,0.1%,0.5% (high precision) |
| Temperature coefficient of resistance | ±25ppm,±50ppm,100ppm (large TCR) |
±1ppm, 5ppm ,10ppm ,25ppm (small TCR) |
| Current noise | Less than +10dB | Less than -20dB |
Resistance tolerance shows possible error in room temperature, and TCR shows resistance change /oC in ppm within a specified temperature range. Chart below illustrates the resistance change of TCR ±10ppm, ±25ppm. TCR range depend on each specification. The resistance change does not have to be the same direction (negative or positive)
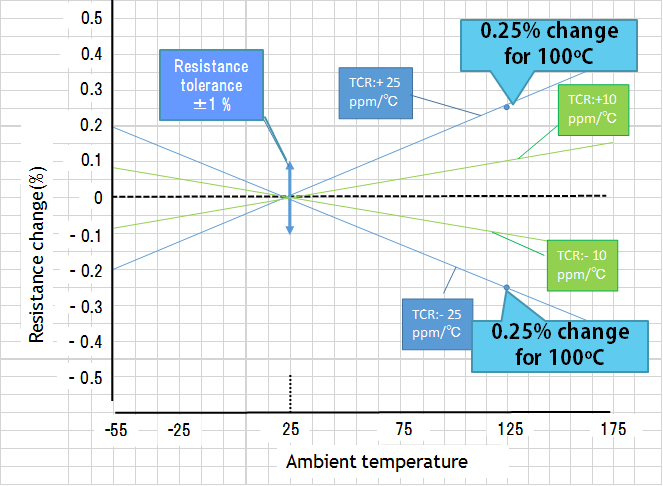
<Resistance tolerance>
・Unit (%) ;±0.1(%) is shown in the chart.
・Tolerance is designated by the following codes.
± 0.01% : (L) ± 0.02% : (P)
± 0.05% : (W) ± 0.1% : (B)
± 0.5% : (D)
<TCR>
・Unit(ppm/℃);±10 , 25
(ppm/℃) are shown in the chart
・TCR is designated by the codes as follows
± 1ppm : (K) ± 2ppm : (L)
± 5ppm : (V) ± 10ppm : (N)
± 25ppm : (P) ± 50ppm : (Q)
Rated Power
Maximum power that can be continuously applied in an ambient temperature. It differs depending on size. Long side terminal and widened terminal products excel in heat dissipation and can handle higher power for the same size, enabling miniaturization or reduction of components.
Rated Voltage
Maximum DC voltage or AC voltage (effective value)that can be continuously applied in an ambient temperature given by the following formula.
E=R×P
E:Rated voltage(V), R:Resistance(Ω), P:Rated power(W)
however, If E is larger than the maximum element voltage, the maximum element voltage is the rated voltage.
Maximum element voltage
Maximum DC or AC voltage(effective value) that can be continuously applied to the resistor.
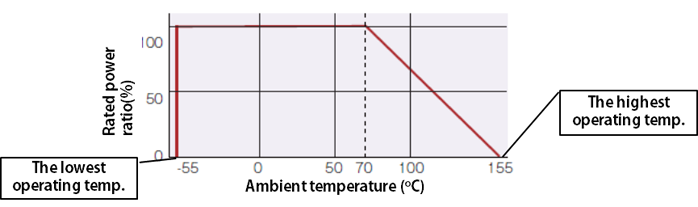
Operating temperature range
The temperature range where, by design, the resistor can be used continuously, defined by the lowest operating temperature and the highest operating temperature.
| The lowest operating temperature: | The lowest temperature where the resistor can be used continuously. |
|---|---|
| The highest operating temperature: | The highest temperature where the resistor can be used continuously.The point where derating curve intersects X axis (zero power) |
Power derating curve
The curve that shows the operating temperature range and maximum power at each temperature point. This curve is dependent of the different product series.